Outline:
Return to Table of
Contents
Goto Installation
The tameroot directory is the root of the directory tree where tame keeps all it's data files and source code files. The tameroot directory is generally named "tame" and the tameroot should never be under the web document area. This is because sensitive customer data and configuration information is stored under this directory. The "tame" directory can be inside a user's account, in the server admin directory, or in virtually any other secure place outside of the web document tree. The placement of this directory in a secure location will protect your system and ensure that it functions effectively.
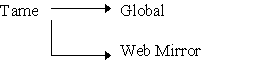
The tameroot directory has two primary sub-directories: global and a web mirror. The global files contains all the program files. The web mirror directory will maintain the mall and shop data as well as all configuration files. This directory is named the same name as the domain, but is not in the web document directory. This directory will be created by the install wizard. If you are installing an update, note the name of your mirror tree as the install wizard will be asking for it. It is important that the mirror directory be located outside of the directories containing your *.tam and *.htm files accessed by web users. This placement provides for the security of your data and configuration files, because the mirror directory is secure from web user access.

Note: Do not use the ATT SMPT server unless you are authorized to do so through a service provider. While our script ships with ATT SMPT server as the default, we do not authorized you to use the server.
In order to function, tame needs read and write permission to several areas. Tame is a cgi program and as such it must run as if it is the same user and in the same group as the httpd server that starts tame.
When the shopping system collects information from a customer, such as the customer's name and address, the information must be stored in a file. In order to create files to store the customer information, tame must have read and write permission to the directories in which the information is stored. Tame stores sensitive customer information in a mirror of the web document tree called the tame mirror. Using mirror directories protects the information from being directly viewed with a web browser. Access would be possible if the information was kept in the web document area.
Shopping system maintenance is completed through the Administration Screens. The web/browser based administration utility allows authorized persons to create new shops, and edit shop and mall configurations. In order for this utility to function, tame needs read and write access to the web document area.
Ultimately, tame needs read and write access to the entire tame mirror tree and to, at least, the web tree root directory in order to fully function.
There are several ways to provide read and write access for the software on UNIX systems. The five methods listed below indicate the level of difficulty to implement and the level of security provided. Other method exist, but these are the most common.
Method 1 : Easiest - least secure
Turn on full (world) read and write access for the tame tree and the web tree. This is the easiest method but is also the least secure. All data files and web documents will be accessible to anyone who has access to the machine. This means there is no control over changes made to your tame files and your database information.
Method 2 : Recommended - secure and flexible
a) Set up the httpd server to run as a specific user. This will usually require setting up an account for the user and changing the server configuration to initiate cgi as that user. Common names for the account are http, httpd, www, web and webadmin.
b) Create a web admin group for tame and web authorized personnel. This group often has the same name as the web account name.
c) Add the httpd server user, the tame install user, and any other authorized users to the web admin group.
d) Change the group status of the entire tame tree and the web document tree to the web admin group.
Note: All the directories in the tame tree must have group read and write status. If tame is only needed in part of the web document area, then only the web document root and the affected areas need write access.
Method 3 : Sticky bit method
Another way to avoid setting up groups is to use setuid to make the tame cgi program run as a particular user.
Set up a tame user account and give that user ownership or group access to the full tame tree and the full web document tree. Make the owner of the tame binary the tame user account. In addition, make the setuid the user and possibly the group on the binary so that when it runs, it will be running as the tame user.
For more on setuid, see the UNIX manual entry for the chmod command.
Note: If you use this method, you will need to setuid the binary each time you update the shopping system. Copying to a setuid file clears the sticky bit.
Method 4 : Easy alternative for method 2 without groups
To avoid the necessity of setting up groups, an alternative is to set up the httpd server as a specific user and give that user ownership of the full tame tree and the full web document tree. Any personnel that need access to the tame/web areas can be given access through the single httpd server account. However, internal accountability is limited with this method because all users enter under the same user name.
Method 5 : Most secure possible - most difficult to set up and use
Method 2 should be adequately secure for most shopping system providers. If method 2 is not adequate, and resources allow, a second server can be set up to run tame admin functions. The second server can be set up on a separate port or a separate domain. Usually a separate port is easiest.
The second server can be set up with user authentication, firewall authentication, or any other means of authentication needed to fully secure the server. The server will need read and write access as outlined in method 2.
The main reason for using this method is to allow the restriction of cgi programs on the normal web server from writing to the web document tree.
There are two standard ways to provide read and write access for the software on NT systems. The methods listed below ensure an effective level of security is provided. Other methods exist, but these are the most common.
Method 1: Providing access using NTFS file permissions and Windows Explorer
Most NT web servers use NTFS file permissions to determine where the web server can read/write/execute. NTFS file permissions are set by selecting file properties from Windows Explorer or the file manager. To ensure that the permissions are set up correctly complete the following steps.
1) Determine the user under which the web server is running by reading the web server documentation.
2) Check permission in the following directories:
- web document tree
- tame tree
- cgi-bin
- system directory: The system directory is the one that contains the cmd.exe or command.com file and is commonly C:\WINNT\SYSTEM32.
3) To allow tame to function correctly set the permissions on your server by using Windows explorer to give the web server user full permissions for these directories. Make sure to check the permissions dialog box that allows application of the permissions to the directory and all files and directories under it.
Example:
A common NT web server is the Microsoft IIS server. This server runs as the user IUSR_NAME where NAME is the assigned machine name. If a machine is named MACHINE the IIS user is IUSR_MACHINE. To provide access use Windows Explorer to give IUSR_MACHINE full permission for the web documents tree, the tame tree, and the cgi-bin.
Method 2: Providing access using NTFS group permissions.
It is also possible to give the web server access by setting up NTFS group permissions. The basic requirements are the same as above. To use this method consult your NT manual for how to set up groups and give users permissions within the group.
![]() Note: If during the install, the TAMICONS
and example shop files fail to be copied to the web directories,
tame probably can not access the cmd.exe file and the copy
command. Check the permissions on your system directory.
Note: If during the install, the TAMICONS
and example shop files fail to be copied to the web directories,
tame probably can not access the cmd.exe file and the copy
command. Check the permissions on your system directory.
created: Katherine C. Davis
3/27/97
edited: Katherine C. Davis 5/20/97